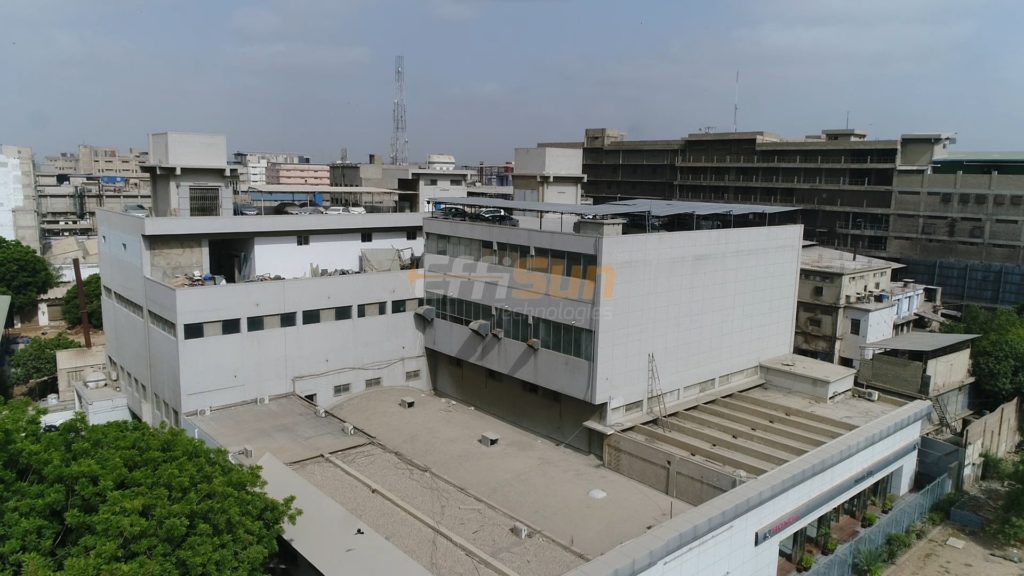
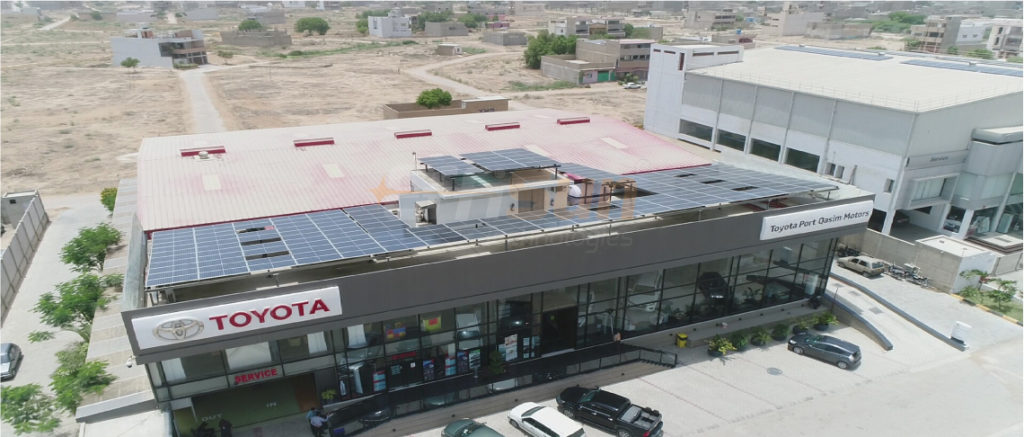
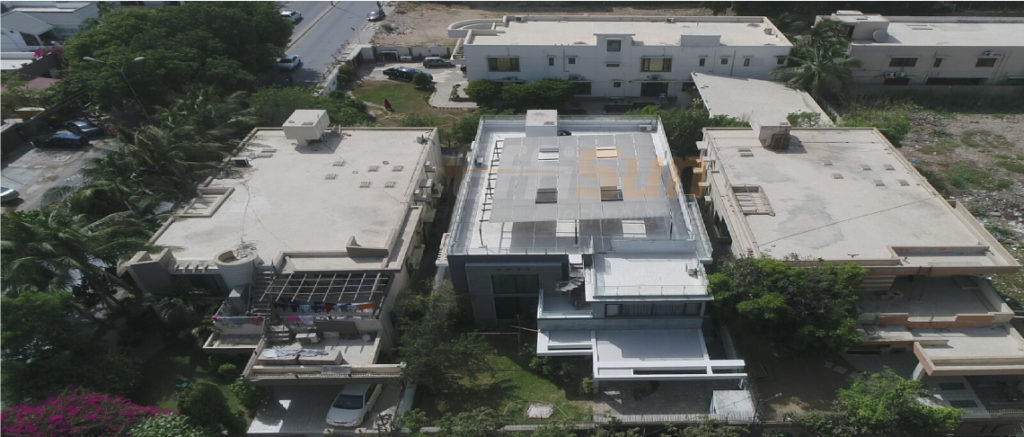
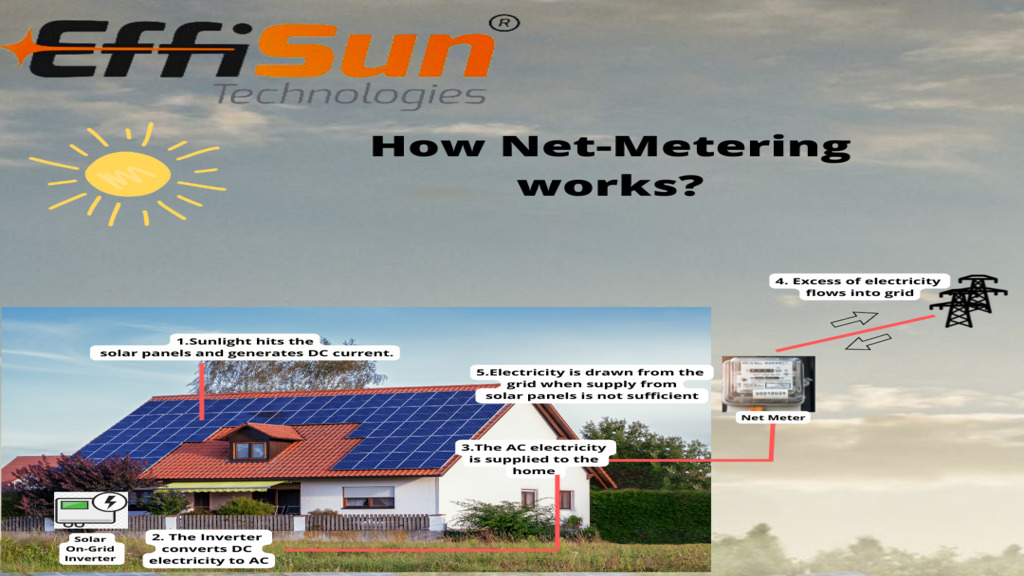
Before transitioning to the modern solar energy system, owners need to understand and have a grip on the concept of net metering. Having a basic understanding becomes pivotal, as this billing mechanism works on the net energy use by a household or a location rather than traditional forward working.
In net metering, solar system owners add back electricity to the grid. This crediting of energy back to the system provides excess energy back to the meter making it go 180-degrees backward. Perhaps an example will suit better in this case.
Putting Net Metering into Perspective
Suppose a residential owner has installed a Photovoltaic (PV) system on their roof. This homeowner’s PV system generates electricity in excess in the daytime, meaning that the household has less energy usage during the day than the electricity being generated by the system. Rather than wasting this excess energy, this homeowner may decide to net-meter his home.
By net metering, the installed electricity meter at the home will then run inverse, crediting the overall electricity usage of the house. In simpler terms, when the household requires additional energy than its average, the excess energy created before will be used again to provide the house with the additional energy it requires. This usually happens at night versus daytime.
This credit of electricity also provides billing advantages for the customers. The billing mechanism will only observe the net usage of electricity by the household providing optimal cost savings. No energy will be wasted in the process and this can also benefit other nearby customers on the grid with their loads.
Control over Utilities and Benefiting Others
It has been found that 20 to 40 percent of an installed solar energy system’s output on average returns to the grid. But this shouldn’t be underestimated as nearby households may also benefit from this energy savings. Also, net metering provides control over electricity bills.
This control over electricity bills by net metering benefits the consumer. As households continue to generate clean and efficient energy by the solar system, net metering provides access to this ‘clean’ energy to that household plus others. As most households with installed solar systems produce excess energy and their supply exceeds demand, net-metered homes give back energy to the grid providing control over utility bills.
Promoting Clean Energy Investments by Net Metering
The economic benefits created by net metering also are attractive. Not only does it provide personal benefits such as control over utility bills and also benefits society at large, but it provides ample investment opportunities for interested parties.
Net metering creates ample demand in the system for this clean energy. This demand further creates demand for related personnel in the industry who work in the domain of solar panels. This means, that the opportunity for investments then naturally leads to the creation of jobs and income.
Job creation and Income opportunities
Solar system manufacturers and installers along with other related jobs will benefit, providing the country with additional jobs and income. It means that such a simple process of generating excess energy by a household contributes to the economy at large, and benefits the whole country and other households by not only excess energy but by providing ample opportunity to work.
The solar supply chain is expanding globally and investments are also thriving in this domain.
Net Metering as Management of Overall Utility Load
It should be kept in mind net metering does not mean lost revenue.
Providing such demand for energy and better management of it creates a smoother supply/demand curve, and peak timings for such loads can be tackled better. Technically, providing consumption and generation from a similar or a nearby point in the vicinity also eases loads on distribution for the energy provider.
The cost-benefit analysis may prove more attractive, but one thing is for certain: solar energy provides value to not only its customers but to society at large.